ALOCASIA SAKONAKHONENSIS
ORIGINAL DESCRIPTION:
Alocasia sakonakhonensis Chatan & Promprom is most similar to Alocasia acuminata Schott (Boyce, 2008; Boyce & Sookchaloem, 2012), but the former is readily distinguishable by the presence of moderately green with numerous dirty mottled dark brown 1–3 mm lines or areas (vs bright green without these dirty mottled dark brown 1–3 mm lines or areas); longer peduncle, spathe, spathe limb, spadix, sterile interstice, and appendix; mostly distinctly 2–4 lobed or rarely unlobed stigma (vs unlobed or very slightly lobed stigma; opened petiolar sheath (vs closed in Alocasia acuminata); dull yellow-brown appendix (vs white one found in Alocasia acuminata).
SYNONYMS: N/A
DISTRIBUTION: Thailand | Sakon Nakhon province in the northeast of Thailand
CLIMATE: Subtropical humid climate
Humidity is moderate throughout the year, ranging from 60% to 70%
Temperature is varies between the seasons - within the range of 48°F/9°C to 88°F/31°C during the day. Minimum temperatures never dip below 45°F/7°C
Rainy and humid season (October to May) and a dry season between June and October. The average annual rainfall is 1,200 mm
ECOLOGY: This new species grows in shaded areas in dry evergreen forests at an elevation of 300–320 m. The plants grow in moist places on limestone, especially along streams.
SPECIES DESCRIPTION:
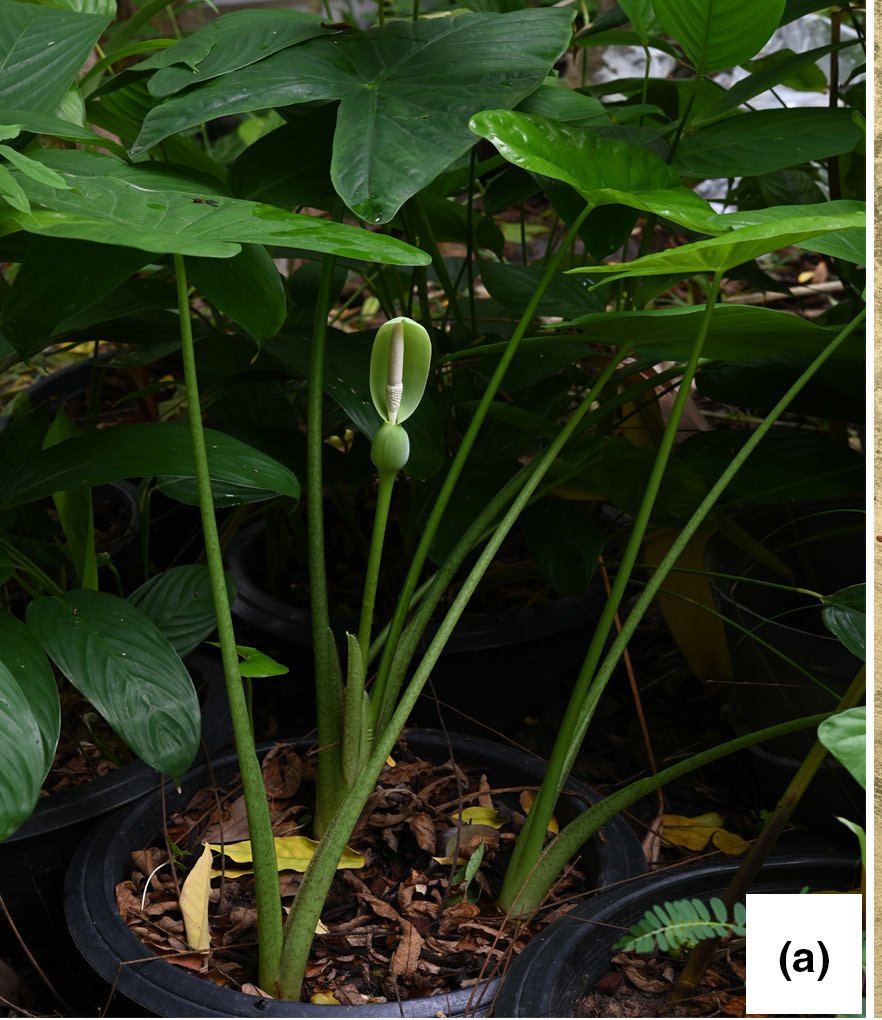
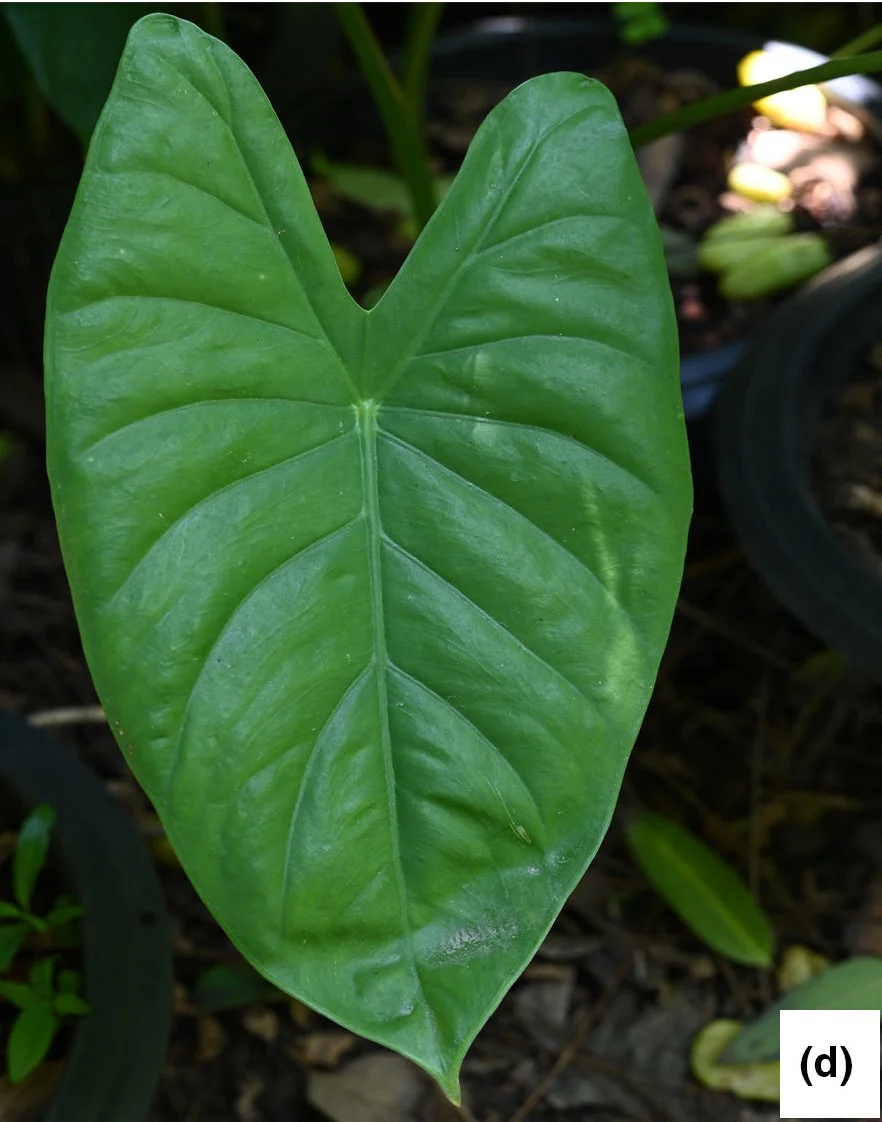
Small to medium-sized, slightly robust, evergreen terrestrial herbs, up to 60 cm tall. Stem rhizomatous, generally elongate, ca. 3–8 cm long and 2.8–3.1 cm diameter, erect and short, inside yellowish-green, older parts covered with remains of old leaf bases and cataphylls; cataphylls 6–8 × 2.5–3.3 cm, green with dirty dark brown spots, glabrous, keel near apex, apex retuse with a small projection, margin entire and translucent. Roots numerous, white. Leaves 2–4 together, subtended by conspicuous lanceolate papery-membranous cataphylls; Cataphylls 14–15 × 1.5–1.8 cm, moderately green with numerous dirty mottled dark brown 1–3 mm lines or areas, glabrous, translucent. Petioles glabrous, moderately green with numerous dirty mottled dark brown 1–3 mm lines or areas, ca. 35–60 cm long (i.e., including sheathing in the lower part ca. 14–18.), sheath closed; lamina spreading, ovate, 20–40 × 14–22 cm, bright green, base slightly hastate to hastate, peltate for 37%–43% of their length; posterior lobes 10–17.5 cm long, apex obtuse; anterior lobe 13–26 cm long, apex cuspidate; anterior costa with 5–7 primary lateral veins on each side, the proximal ones diverging at ca. (50°–) 60–80°, the angle decreasing in distal veins and the course more or less straight to the margin; axillary glands hardly conspicuous abaxially; secondary venation initially wide-spreading, then sooner or later deflected toward the margin; interprimary collecting veins weakly defined. Inflorescences usually solitary. Peduncles 25–30 cm long, moderately green with numerous dirty mottled dark brown 1–3 mm lines or areas, erect at first, then declinate, elongating and then erect in advanced fruit, subtended by 1–2 cataphylls; the cataphylls linear-lanceolate, 16.5–18.5 × 2.5–2.6 cm, keel near apex, apiculate apex, translucent.
INFLORESCENCE:
Spathe 13.0–14.5 × 3.0 cm, moderately constricted ca. 3.5–4.0 cm from the base; lower part of spathe bright green, ovoid; limb lanceolate, canoe-shaped and longitudinally hooded, 9.5–10.5 × 2.3–2.5 cm, apex apiculate, membranaceous, very pale green. Spadix shorter than the spathe, ca. 11–12 cm long, sessile; female flower zone 1.0–1.2 cm; ovary globose, slightly 3-lobed- globose or depressed globose or slightly elliptic, 2–3 mm diam., light green; style 1.2–1.5 mm long; stigma off-white with a hint of yellow or strong pale yellow, distinctly 2–4 lobed or rarely unlobed; sterile interstice subcylindrical, 23–25 mm, narrower than the fertile zones, corresponding with the spathe constriction, off-white with a hint of yellow or strong pale yellow; lower and upper synandrodia often with incompletely connate staminodes, flat-topped; male flower zone subcylindric, 2.0–2.3 × 6–7 mm, off-white with a hint of yellow or strong pale yellow; synandria 4–8-merous, more or less hexagonal to circular, 1.5–4.0 mm diam.; appendix 5.0–5.2 cm long, slightly narrower than male flower zone, cylindrical lower part ca. 2/3, elongate-conic upper part ca. 1/3, dull yellow-brown. Fruiting spathe ovoid, ca. 14 cm long, green. Fruits globose-ellipsoid, ca. 0.7–0.8 cm diameter, green, ripened orange-red.
The flowering period is from May to June, and the fruiting period is June to July.
VARIEGATED FORMS: N/A
ETYMOLOGY: The specific epithet of Alocasia sakonakhonensis refers to the type locality, the Sakon Nakhon province in the northeast of Thailand (Thai: สกลนคร)
NOTES:
Alocasia sakonakhonensis has not been recorded or described so far. This species grew in two small populations under the forest canopy in Sakon Nakhon province at an altitude of 300–380 m. The plant is estimated to have fewer than 2500 mature individuals, with each subpopulation consisting of fewer than 250 mature individuals. Therefore, it should be considered as “Endangered (EN),” according to IUCN criteria C(C2ai) (IUCN Standards and Petitions Committee, 2024).
Alocasia sakonakhonensis represents a non-pachycaul herbaceous taxon. It shares vegetative similarities with Alocasia acuminata, characterized by non-seasonal dormancy, the absence of pachycaul and basal branching, short internodes, and peltate, bright green leaf blades. However, in terms of morphology, the new species can be readily distinguished from the latter. This distinction is evident in the moderately green color of the petiole and peduncle, which feature numerous dirty mottled dark brown lines or areas measuring 1–3 mm (as opposed to the bright green color without such lines). Additionally, the length of these organs—including the peduncle, spathe, spathe limb, spadix, sterile interstice, and appendix—differs in Alocasia sakonakhonensis , being more extended than those found in A. acuminata (measuring 25–28 cm, 13.0–14.5 cm, 9.5–10.5 cm, 11–12 cm, 23–25 cm, and 5.0–5.2 cm in length, respectively). The stigma of Alocasia sakonakhonensis is distinctly 2–4 lobed, very rarely unlobed (in contrast to A. acuminata, which is very slightly unlobed). Furthermore, the petiolar sheaths of Alocasia sakonakhonensis are open, unlike those of A. acuminata, which are closed. In A. acuminata, the appendix exhibits a dull yellow-brown color (compared to the white color in A. acuminata). Additional details regarding the morphological distinctions between Alocasia sakonakhonensis and A. acuminata are presented in Table 1. Below is a modified key to the non-pachycaul herbaceous taxa of Alocasia in Thailand, adapted from Boyce and Sookchaloem (2012).
CULTIVARS: N/A
HYBRIDS: N/A